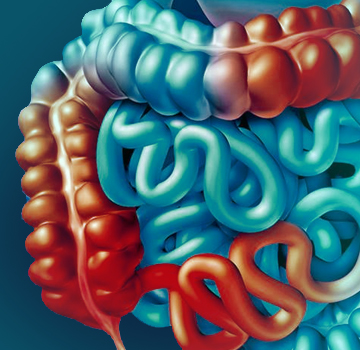
Intestinal
Diseases
We still do not fully know its cause, however, we do know that it is related to a malfunction of the immune system, where the body itself detects bacteria from the intestinal flora as harmful, causing inflammation of the digestive system.
Irritable bowel syndrome
It is a common disorder that affects the large intestine. It is a chronic condition of abdominal pain or discomfort associated with alterations in bowel habits.
It can appear after a severe episode of diarrhea (gastroenteritis) caused by bacteria or viruses. There may be other triggers as well, including stress.
Symptoms: Abdominal pain of more than 3 months duration, bloating or swelling after eating, periods of constipation alternating with diarrhea, change in the shape and/or consistency of bowel movements.
Constipation
Constipation is considered when there are three or fewer bowel movements per week, with hard and dry or lumpy stools. The sensation of incomplete evacuation can also be experienced and is also considered constipation.
It can present chronically if the aforementioned symptoms manifest for at least three months or acute if it develops in isolation.
Symptoms: Less than three bowel movements a week, hard, dry or lumpy stools, difficulty or pain in passing stools, feeling that the bowel movements were not complete, malaise or back pain, abdominal swelling, lack of energy.
Chronic diarrhea
It is one that occurs for a period of more than 4 weeks, with a decrease in the consistency of the feces or an increase in the number of evacuations.
The main symptom of chronic diarrhea is the increase in the frequency with which the affected person will have to go to the bathroom. In turn, the consistency of the stool will gradually decrease, abdominal pain, that is, those commonly known as cramps, nausea or vomiting, fever.
In the event that the diarrhea is very abundant, dehydration can occur due to the abundant loss of fluids. Dehydration can be recognized by the following: extreme tiredness, thirst, dry mouth, dry tongue, muscle cramps, dizziness, weak urine concentration.
Nonspecific chronic ulcerative colitis UC
It is an inflammatory disease of the colon (large intestine). It is characterized by inflammation and ulceration of the interior wall of the colon. Typical symptoms include diarrhea (sometimes bloody) and often abdominal pain.
Symptoms: Depending on the extension of the colon that is affected and the severity of said affectation. There are intestinal and extra intestinal symptoms of UC disease.
Among the most frequent are: Diarrhea with mucus and presence of blood in the stool, rectal urgency (imperative urge to defecate with barely being able to contain it), tenesmus (continuous feeling of wanting to defecate that does not end up alleviating even after evacuation), pain abdominal.
Crohn's disease
It affects the small and large intestine, it is a chronic and inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal tract. This disease is extremely invasive and compromises all layers of the intestinal wall, including the mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa.
It is most likely caused by dysregulation of the immune system, genetic, environmental, dietary, and infectious factors, and its symptoms are similar to those of ulcerative colitis: Abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, weight loss, weakness due to malabsorption of nutrients.
Diagnosis is made by clinical examination and patient history and endoscopy. The treatment is established taking into account the evolution of the disease, and although there is no cure, periods of remission may occur.
Types of bowel disease
Within inflammatory bowel disease we find two different types: ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. The latter can affect any section of the digestive system, while Ulcerative Colitis affects only the colon.