Gynecological
Surgery
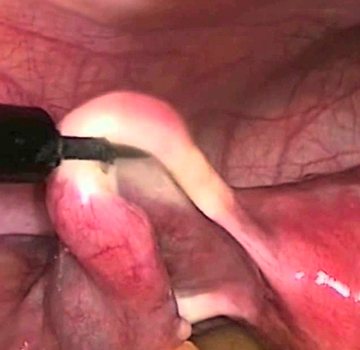
Laparoscopic and gynecological surgery allows the treatment of diseases of the internal and external genitalia. This type of treatment allows solving cases such as ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, uterine pathology and also pelvic floor pathology.
Salpingoclasia
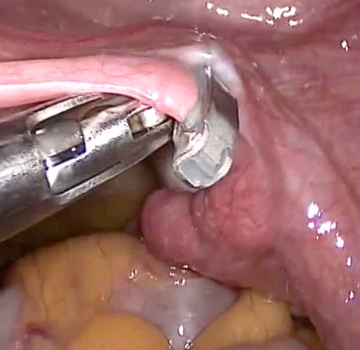
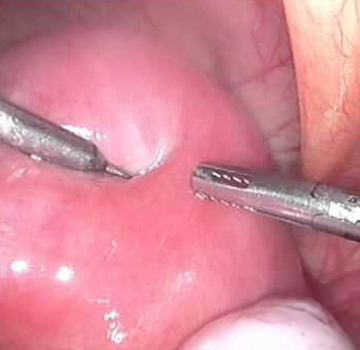
It is a female contraceptive method which some time ago was not reversible. It consists of ligating and sectioning the uterine tube in order to prevent the sperm from meeting the egg and thus preventing fertilization and pregnancy.
Things you should know about salpingoclasm:I
It consists of cutting or tying the tubes to prevent the passage of sperm to the egg and inhibit fertilization, it is a definitive and irreversible contraceptive method, its percentage of action exceeds 99% success, since it is not a hormonal contraceptive it does not prevent lactation It does not harm health, it does not interfere with libido or sexual relations, it favors the enjoyment of sexual intercourse, eliminating the fear of pregnancy and the use of other contraceptive methods, it reduces the risk of pelvic inflammation and the risk of cancer. of ovary.
It is performed through an outpatient intervention and involves a postoperative period with rapid recovery.
Fibroids
They are benign tumors that develop on the walls of the uterus. Its incidence is high, more than 40% of women of childbearing age suffer from it, but its treatment is only necessary when symptoms such as excessive bleeding or severe discomfort in the area occur.
A valid and effective and minimally invasive technique for its elimination is embolization, which consists of obstructing the blood supply that reaches the fibroid, achieving its metabolic inactivation and its subsequent reduction. With this technique, several fibroids can be treated at the same time if necessary, and it also has a shorter postoperative recovery period than in conventional surgery.
Open hysterectomy
It consists of the removal of the uterus or womb, the organ inside which the fetus develops. Sometimes, in women who have already gone through menopause, when removing the uterus, the fallopian tubes, which are the tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus, are also removed (called salpingectomy), and the ovaries, which are called an oophorectomy.
This is done to prevent ovarian cancer from developing and reduce the risk of developing breast cancer. However, in women who have not yet gone through menopause, removal of the ovaries is associated with induction of menopause and an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis.
Breast biopsy
It is the removal or removal of breast tissue for the purpose of examining it for signs of breast cancer or other disorders. Breast cysts and fibroadenomas are quite common in the female population.
In cases where they are very small, they can be managed conservatively, however, in cases where they can be felt with the hand, grow, have a family history or simply bother the patient, excisional biopsies can be performed. to remove those cysts or fibroadenomas through small wounds.
Ectopic pregnancy
It occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the uterus. Ectopic pregnancies most often occur in one of the fallopian tubes. If the fertilized egg continues to grow in the fallopian tube, this can cause the tube to rupture. Heavy bleeding inside the abdomen is likely.
Symptoms: Abnormal vaginal bleeding, mild cramping on one side of the pelvis, no periods, pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area The procedure to treat an ectopic pregnancy is surgical using laparoscopy or laparotomy.
Gynecological surgical techniques
Gynecological surgery can be abdominal, vaginal, and endoscopic or laparoscopic.
Laparoscopic surgery is minimally invasive, and its recovery requires a shorter hospital stay.
Vaginal endoscopy called hysteroscopy, allows the diagnosis and treatment of polyps, fibroids, and uterine malformations.
The vaginal addresses the treatment of genital prolapse, pelvic floor pathology, and/or surgery for urinary incontinence.
Abdominal surgery continues to be a suitable option when the previous techniques are not indicated or the surgeon cannot obtain the same treatment or safety results.