Oncological
Surgery
In an advanced stage, it is the responsibility of the oncologist surgeon to help in the staging or staging of the cancer. That is, determine how extensive the tumor is, whether it has invaded locally, or has spread via the lymphatics to lymph nodes or via the blood to other organs.
Colon cancer
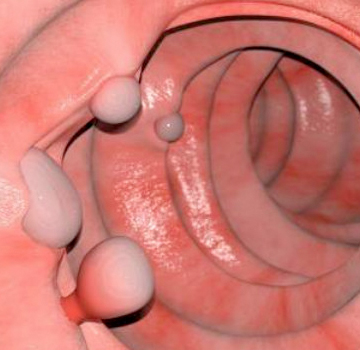
It is the growth of a malignant tumor that affects the section of the intestine also known as the large intestine. This section runs from the end of the small intestine to the beginning of the rectum.
Sometimes colon cancer also affects the rectal area and this disease is referred to as colorectal cancer. In its early stages, it does not present symptoms, it begins with a growth of tissue or a tumor called a non-cancerous polyp, which, when it spreads and grows, can become cancerous.
Treatment when colon cancer has already been diagnosed is directed at removing all cancerous tissue through surgery.
Thyroid cancer
It is characterized by having a slow course (differentiated thyroid cancer, papillary or follicular type), however the most aggressive forms (anaplastic cancer for example) can substantially reduce the survival of those who suffer from it.
Warning signs and symptoms: difficulty swallowing or breathing, changes in the tone of voice, cough, pain in the neck, jaw or ears, appearance of suspicious cervical lymph nodes.
Thyroid surgery is performed when there is cancer, large goiters with compressive symptoms such as difficulty breathing or swallowing, and hyperthyroidism refractory to clinical treatment.
Neck tumors
Due to their location and consequences, these are tumors with a great impact on the quality of life of patients, being able to affect eating, speaking, breathing and physical appearance.
The warning signs that can make someone suspect that they need to see a specialist, especially if they are a smoker or drink alcohol frequently, are: presenting hoarseness (voice disturbance), having a mouth wound that does not heal in 15 days, pain in the pharynx that radiates to the ear, persistent discomfort when swallowing or the continuous sensation of a foreign body in the throat, the appearance of a suspicious lump in the neck.
Treatment usually requires surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy; and the focus of its approach and recovery must be multidisciplinary, involving speech therapists, speech therapists, nutritionists, endocrinologists, pathologists, psycho-oncologists and specialized nursing.
Biopsies
A suction biopsy is less invasive than open or closed surgical biopsies, both of which involve a more extensive skin incision and local or general anesthesia. The procedure is generally painless and the results are as accurate as those obtained by surgical removal of a tissue sample.
The recovery period is short and patients can soon resume their usual activities.
Our services: breast biopsy, prostate biopsy, thyroid biopsy
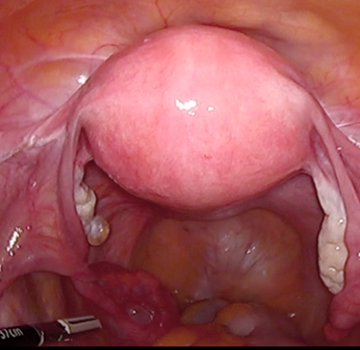
Ovarian tumors
Ovarian tumors have abnormal cells that can turn into cancer, but usually don't. Usually, this disease remains in the ovary.
When disease is found in one ovary, the other ovary should also be examined for signs of disease.
Laparoscopy is the most common procedure used to remove tumors through a small incision in the abdomen, using a laparoscope.
Instead of using a large abdominal incision, an instrument is inserted through a small incision. Typically, little or no scarring occurs.
Surgical techniques
In certain types of cancer, cytoreductive surgery is indicated, the objective of which is to remove as much visible cancer as possible (gross disease) and then continue with other treatments, such as chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy. Surgery can improve quality of life by relieving pain, obstruction, or other complications caused by disseminated disease.